Big Tech Drives the Stock Market Without Much U.S. Help
The Fang stocks get lots of their sales from countries that are doing better at managing the pandemic and reopening.
Bloomberg, July 13, 2020
The stock market has been on a tear for the past three months — and Big Tech deserves much of the credit.
But how can this possibly be, when the coronavirus has inflicted so much damage on the U.S. economy, with the highest unemployment since the Great Depression and gross domestic product headed into a black hole? And anyway, it’s not as if tech is untethered from the economy.
Yet, maybe tech isn’t all that dependent on growth in the U.S.
Compared to the rest of the world, and for the first time in ages, many wealthy industrialized countries are doing better — and in some cases, much better — than the U.S. Nations such as Japan, South Korea and Germany not only have managed to contain the pandemic, but their economies are well ahead of the U.S.’s into their re-openings.
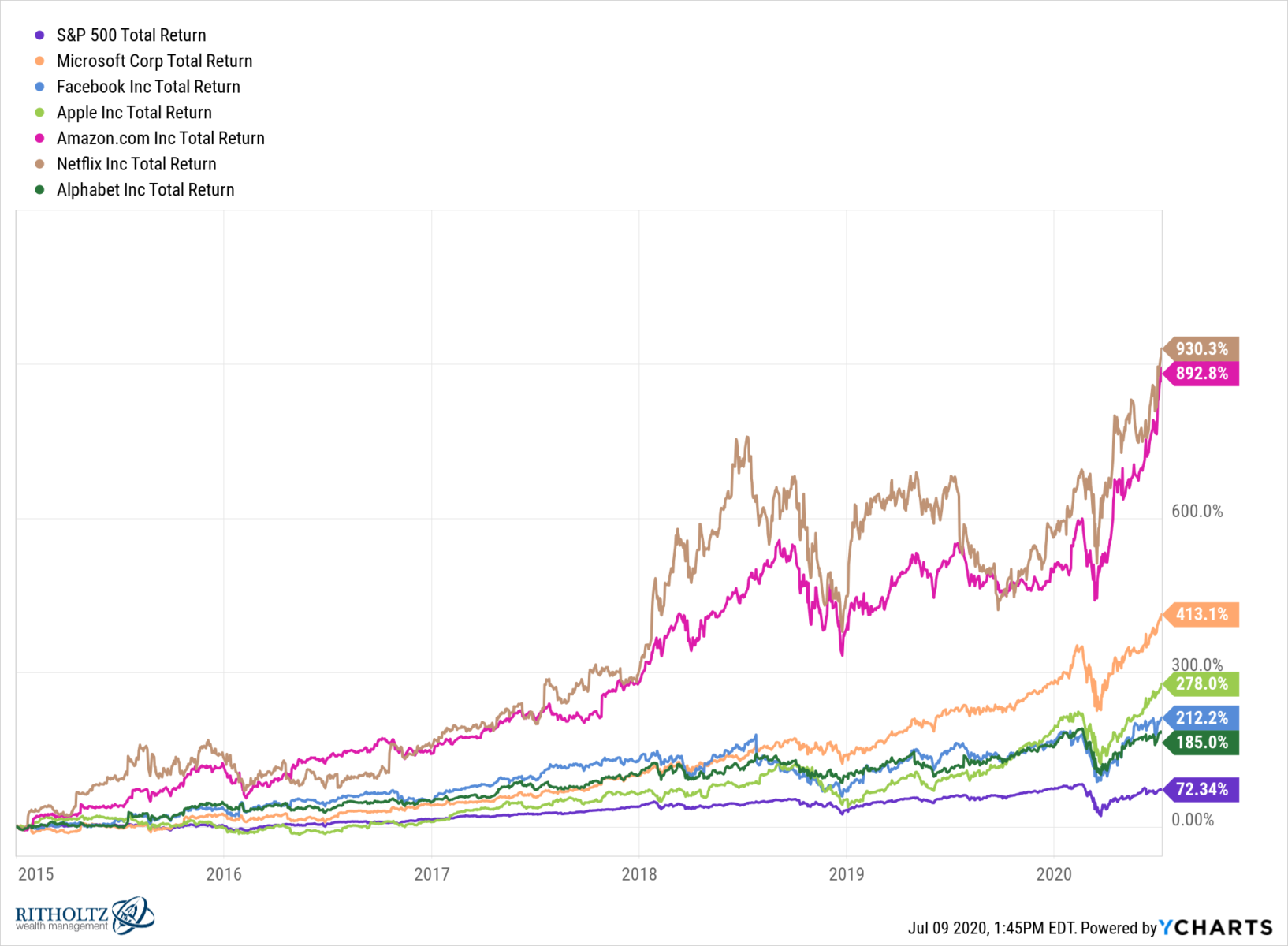
For the past five years, a small group of tech stocks has had an outsized influence on U.S. markets. Two-thirds of the gains in the S&P500 have been driven by just six U.S. companies — Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google (Alphabet) — the so-called FAANG stocks — and Microsoft. An index of those six stocks is up more than 62% since the March lows, while the S&P 5001 is up about 40%:
Overseas markets may very well be a key reason shares of the biggest U.S. tech companies are powering higher. These tech companies derive a surprisingly large share of their revenue from foreign markets. According to Standard & Poor’s, companies in the S&P 500 derived 42.9% of their sales from overseas markets in 2018 (2019 data is not yet available).
But this share is much higher for the big tech companies: Apple generated more that 55% of its revenue outside the U.S. in the year ended in September; in some quarters, overseas accounted for as much as 60% of revenue. International accounted for 54.5% and 53.8% of Facebook and Alphabet revenues, respectively. For Microsoft and Netflix, the split is about half domestic and half overseas (49.0% and 49.4%, respectively). Amazon is the Big Tech exception, generating a sizable majority of its revenue within the U.S.
What make overseas so important, though, is because that’s where the growth is. Netflix had revenue growth of 21% in 2019, but the domestic side was a laggard at just 7%. Facebook, meanwhile, now has more users in India than in the U.S., with Indonesia and Brazil growing fast. For Alphabet, Asia and Latin America have produced faster revenue growth than the U.S.
It isn’t a coincidence that these companies that are so reliant on the rest of the globe have seen their stock prices do well. The Covid-19 numbers suggest that much of the world is way ahead of the U.S. not only in terms of managing the pandemics, and that their economies are recovering faster.
As of July 9, globally, there were more than 12 million confirmed cases of Covid-19 and almost 550,000 deaths. In the U.S. those figures were 3 million confirmed cases and 132,000 deaths. This data is a report card on how well the country is managing the pandemic: The U.S. has 4.2% of the world’s population, but 25% of the infections and 24% of the deaths.
And yet, even this national incompetence has worked to the advantage of the Big Tech companies. All they require of their customers is a computing device and a network connection; users are not limited by geography — either domestically or internationally. Nor do users need to have a physical presence at an office.
Some companies are well positioned to survive the pandemic lockdown, thriving during an era of remote work and social distancing. Many of these same companies are well positioned to benefit from the rest of the world’s economic recovery. As it turns out, tech companies can profit both from the U.S.’s shutdown and a recovering Europe and Asia. It is a very effective one-two punch. It explains so much of the market’s gains.
_______
1. For the 5-year period since 2015 inclusive, the S&P500 index gained 56.5%. Since the March 23rd lows this year, the index is up 42.1%, about three quarters of the gains of the prior 5 years.
~~~
I originally published this at Bloomberg, July 13, 2020. All of my Bloomberg columns can be found here and here.